Reduction in running costs = CO2 capture costs
I support capturing and reusing the CO2 that has already been generated without releasing it into the atmosphere, but it would be pointless to generate CO2 in order to obtain the energy to capture it. Captured CO2 gas is the same as air and cannot be stored or transported as is. Generally, CO2 is compressed and then liquefied to make it compact. This compression and liquefaction process generates waste heat called compression heat and condensation heat. This is physically unavoidable, but the technology proposed by G.V.Lab. uses this waste heat as energy for equipment that separates, concentrates and captures CO2 from the air, which can reduce the cost of CO2 capture.
Initial cost reduction
Even if it is possible to reduce the cost of CO2 capture, expensive equipment cannot be depreciated and is unlikely to become widespread.
G.V.Lab.'s CO2 separation, concentration and capture equipment was developed with reducing initial costs as a priority from the development stage. This is because high costs are roughly correlated with the amount of CO2 emissions when manufacturing CO2 capture equipment, and expensive equipment means that a lot of CO2 is generated during the manufacturing process.
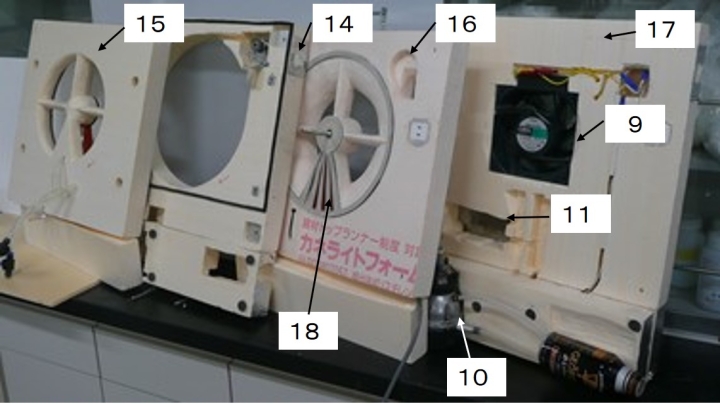
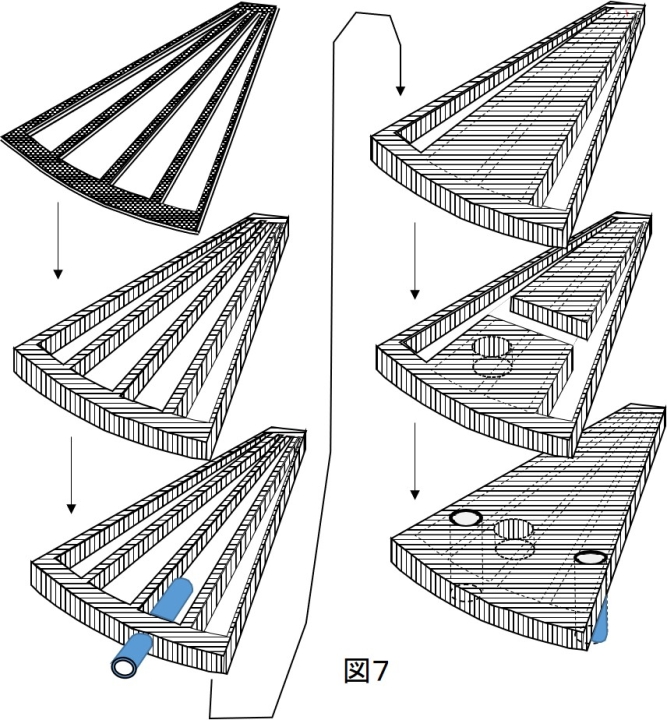
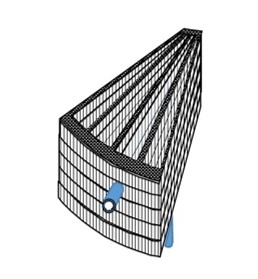
1. The casing is integrated with a laminated structure of insulating foam plates. For example, it is composed of a front panel A, a B panel that houses the rotor, a rear panel C, and a D panel where the fan is attached. Each panel is mass-produced by foam molding. The device is completed by attaching parts to each panel and finally laminating them together.
2. The complex desorption, recovery, and purge zones required to achieve the high performance of Wet-TSA are inexpensively constructed with a laminated structure of foamed silicone sheets, which ensures insulation while at the same time providing flexible sealing properties.
Reduce maintenance and management costs
The fact that CO2 separation and concentration recovery equipment is inexpensive and easy to dispose of when discarded is not enough to be considered. Maintenance costs such as maintenance and replacement of replacement parts must not be forgotten. G.V.Lab.'s CO2 separation and concentration recovery equipment is configured to have a large capacity by accumulating small and lightweight equipment , so there is no need to plan large-scale construction schedules or use cranes, as is the case with the replacement of large equipment. Maintenance can be done by workers alone, such as partial replacement at appropriate times, such as with the filter unit of an air conditioning unit. Simply remove the unit that needs to be replaced and install the unit that has been completed with maintenance. The removed unit can be taken back to the factory, and durable parts can be replaced or repaired, and it can be stored in preparation for the next maintenance.
Reduce disposal costs
In recent years, solar power generation, EVs, and other technologies have been attracting attention as a measure to reduce CO2 emissions, and their development, commercialization, and widespread use are progressing rapidly. However, at the same time, waste disposal and recovery measures have been delayed, and there is growing concern that the future large environmental burden and the associated cost burden will be passed on to future generations.
The atmospheric CO2 capture and concentration device proposed by G.V.Lab. has been considering this point since the development stage.
1. Lightweight and easy to carry, making it easy to collect from the installation site
2. Easy to disassemble after collection and separate into metals, combustibles, etc.